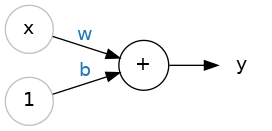

x, what reaches the neuron is w * x.y = w * x + b, or as a formula y = wx + b. We know it on math, it’s a linear equation, where w is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
y = outputx = inputw = weightb = biasMultiple inputs
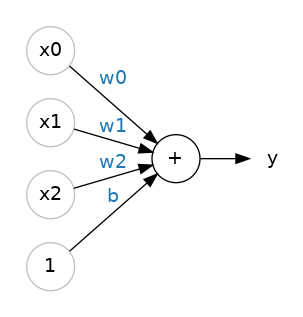
y= w0x0 + w1x1 + w2x2 + b.(ChatGPT) The bias is not counted as an input. It’s a separate term.(ChatGPT The **bias** is not counted as an input (it's a constant) but shifts the hyperplane.Code example for analogy of measuring calories (output) with combination of sugars, fiber, and protein (input):
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Create a network with 1 linear unit
model = keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(units=1, input_shape=[3])
])
Becomes
calories = keras.Sequential([
// units=1, means there is only one neuron
// input_shape=3, for the model accept sugar, fiber, and protein as input
layers.Dense(units=1, input_shape=[3])
])
Why is
input_shapea Python list?
The data we’ll use in this course will be tabular data, like in a Pandas dataframe. We’ll have one input for each feature in the dataset. The features are arranged by column, so we’ll always haveinput_shape=[num_columns]. The reason Keras uses a list here is to permit use of more complex datasets. Image data, for instance, might need three dimensions:[height, width, channels].
(ChatGPT) All **weights** are stored in **tensors**, but Not all **tensors** are weights (they could be inputs, outputs, gradients, etc.) Think of a **weight** as a **role**, and a **tensor** as a **container**.(ChatGPT) Tensors are data structures that store numbers in 0D, 1D, 2D, or more dimensions. They are the fundamental building blocks of data in deep learning.

Applying Rectified to a linear unit becomes rectified linear unit or ReLU. Hence, the formula becomes max(0, w * x + b) or max(0, wx + b)
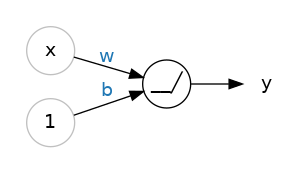
Code example:
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
model = keras.Sequential([
# the hidden ReLU layers
layers.Dense(units=4, activation='relu', input_shape=[2]),
layers.Dense(units=3, activation='relu'),
# the linear output layer
layers.Dense(units=1),
])
activation argument.Set the epoch more than we need, to prevent overfitting where the model learns too long, and to prevent underfitting where the model hasn’t learned long enough. So, let the Keras do the work with early stopping.